|
Be the first user to complete this post
|
Add to List |
324. Stack Data Structure – Introduction and Implementation
What is Stack??
- Stack is an abstract data type (ADT) and very useful in programming.
- In computer science, a stack is an abstract data type that serves as a collection of elements.
- Majorly all the operations are done at only one end of the stack which is top of the stack.
- The order in which elements in stack are stored is with LIFO (Last-in-First-Out) manner. Means the element inserted last will be removed first.
See the diagram below for more understanding.
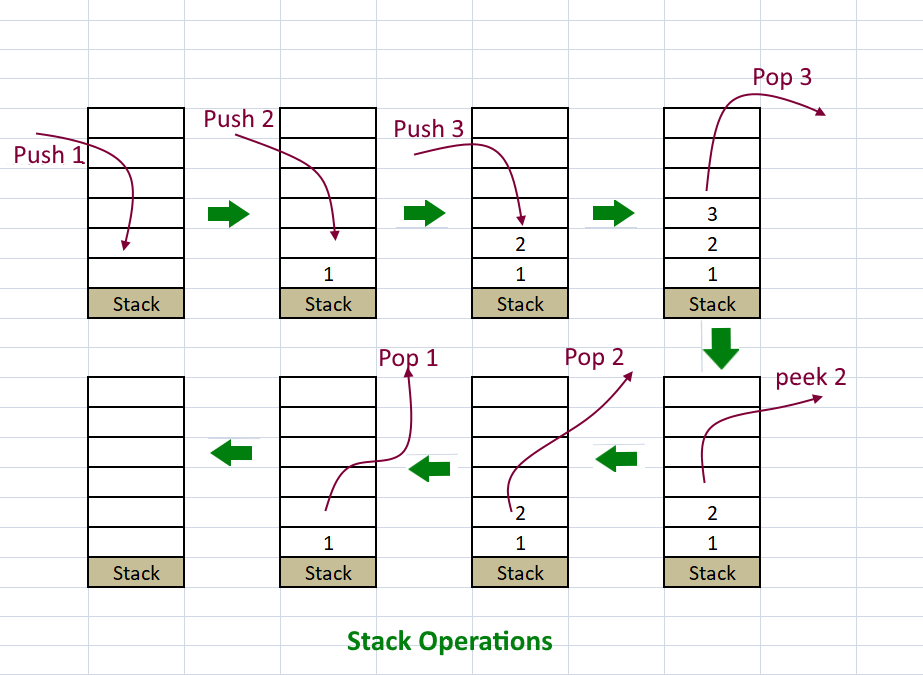
Operations on Stack and How to Implement:
Java already has a built-in class for Stack. Click here to read about it.
Ways to implement Stack
- Implement stack using Array (discussed in this article)
- Implement stack using LinkedList
Operations:
Initialize a topIndex = -1;
- For push() operation- increment topIndex by 1 and add element at this index in array. Time- O(1)
- For pop() operation- remove element from the topIndex, decrement topIndex by. Time- O(1)
- For peek() operation- return the element from the topIndex. Time- O(1)
- For isEmpty() operation- check if topIndex<0 then return true else false. Time- O(1)
- For getSize() operation- return the topindex+1. Time- O(1)
Output:
Is Stack Empty: true Inserting 1 into Stack. Inserting 2 into Stack. Inserting 3 into Stack. Inserting 4 into Stack. Stack overflow, ...cannot insert new element Stack (top-->bottom): 4 3 2 1 Popping from Stack. Popped Element: 4 Popping from Stack. Popped Element: 3 Stack (top-->bottom): 2 1 Inserting 6 into Stack. Popping from Stack. Peeking Element: 6 Stack (top-->bottom): 6 2 1 Is Stack Empty: false Stack Size: 3

