|
Be the first user to complete this post
|
Add to List |
194. Introduction to Threaded Binary Tree
What is a Threaded Binary Tree??
A binary tree is threaded by making all right child pointers that would normally be a null point to the inorder successor of the node (if it exists), and all left child pointers that would normally be a null point to the inorder predecessor of the node.
- We have the pointers reference the next node in an inorder traversal; called threads
- We need to know if a pointer is an actual link or a thread, so we keep a boolean for each pointer
Why do we need a Threaded Binary Tree?
- Binary trees have a lot of wasted space: the leaf nodes each have 2 null pointers. We can use these pointers to help us in inorder traversals.
- The threaded binary tree makes the tree traversal faster since we do not need stack or recursion for traversal
Types of threaded binary trees:
- Single Threaded: each node is threaded towards either the in-order predecessor or successor (left or right) means all right null pointers will point to the in-order successor OR all left null pointers will point to the in-order predecessor.
- Double threaded: each node is threaded towards both the in-order predecessor and successor (left and right) means all right null pointers will point to the in-order successor AND all left null pointers will point to the in-order predecessor.
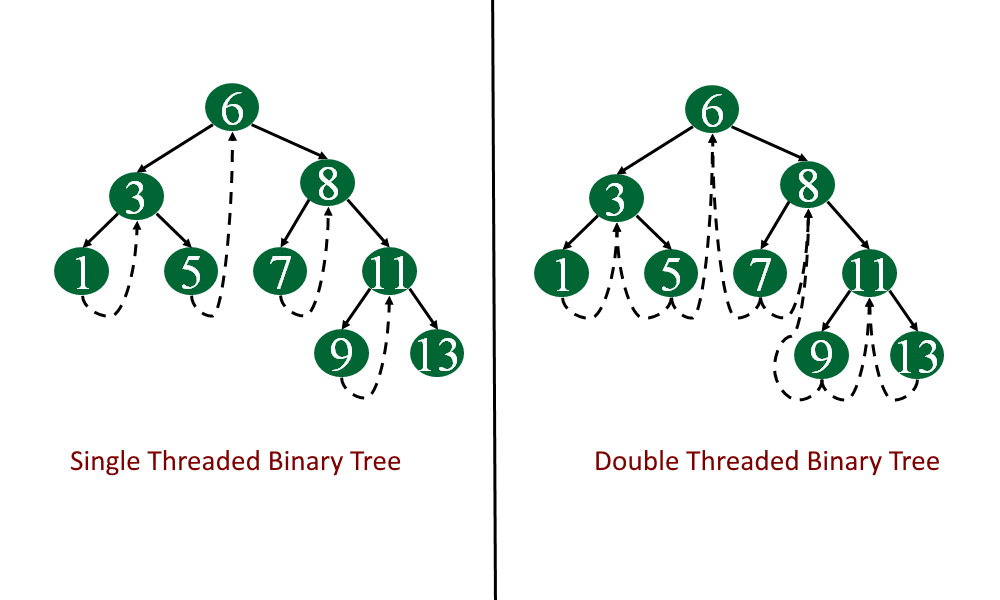
We will see the complete implementation of both types in the next articles - Single threaded binary tree, double threaded binary tree
Source:
http://web.eecs.umich.edu/~akamil/teaching/su02/080802.ppt

