|
This post is completed by 3 users
|
Add to List |
163. Dynamic Programming - Maximum size square sub-matrix with all 1s
Objective: Given a matrix of 0's and 1's (binary matrix). Find out the Maximum size square sub-matrix with all 1's.
Example:
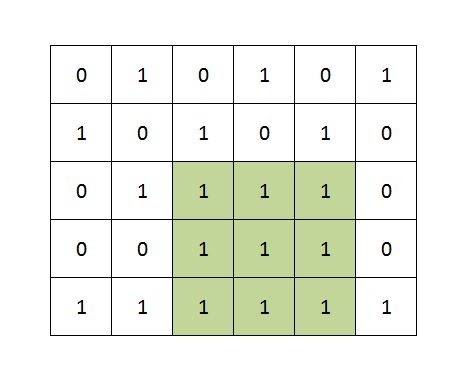
Approach:
Base Cases:
- If only one row is given then cells with 1's will be the Maximum size square sub-matrix with size = 1.
- If only one column is given then cells with 1's will be the Maximum size square sub-matrix with size = 1.
Dynamic Programming (Bottom-up).
- Create an auxiliary array of the same size as the given input array. We will fill the auxiliary array with Maximum size square sub-matrix with all 1's possible with respect to the particular cell.
- Once the auxiliary is filled, scan it and find out the maximum entry in it, this will be the size of the Maximum size square sub-matrix with all 1's in the given matrix.
How to fill the auxiliary matrix??
- Copy the first row and first column from the given array to the auxiliary array. (Read the base cases described earlier).
- For filling the rest of the cells, check if a particular cell's value is 0 in the given array, if yes then put 0 against that cell in the auxiliary array.
- check if a particular cell's value is 1 in the given array, if yes then put Minimum (value in the left cell, top cell, and left-top diagonal cell) + 1 in the auxiliary cell.
Recursive Equation:
For Given arrA[][], create auxiliary array sub[][].
Base Cases:
sub[i][0] = arrA[i][0] i = 0 to row Count // copy the first column
sub[0][i] = arrA[0][i] i = 0 to column Count // copy the first row
for rest of the cells
sub[i][j] = 0 if arrA[i][j]=0 = Min(arrA[i-1][j], arrA[i][j-1], arrA[i-1][j-1] )
At the End, scan the sub[][] and find out the maximum entry in it.
Example:
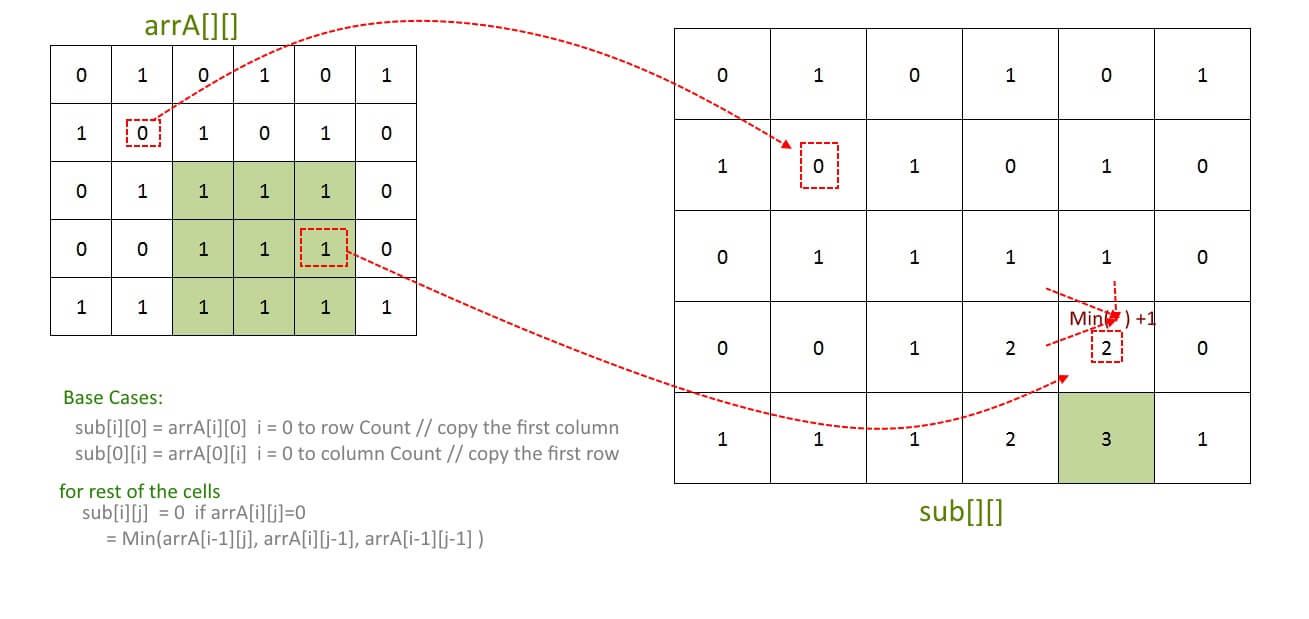
Output:
Output: Maximum size square sub-matrix with all 1s: 3

